Our technical definitions explain common technical terminology used in the Honeywell Test & Measurement products and application.
Absolute Pressure Transducer:
A pressure transducer or pressure sensor that has an internal reference chamber sealed at or close to 0 psia (full vacuum) and normally provides increasing output voltage for increases in pressure.
Accuracy:
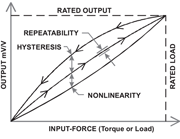
The combined error of nonlinearity, repeatability and hysteresis expressed as a percent of full scale output.
Figure 1. Accuracy Drawing
Axial Load:
A load applied along or parallel to and concentric with the primary axis.
Bridge:
A Wheatstone bridge configuration using four active strain gauges.
Figure 2. Bridge Drawing

Bridge Resistance:
The nominal value of the individual legs that make up a complete Wheatstone bridge.
Calibration:
The comparison of transducer voltage outputs against the outputs of a reference standard.
Damping:
The reduction of response at the resonant frequency through the use of a damping media, such as oil. This is usually specified as the ratio of critical damping.
Dead Volume:
The volume inside the pressure port of a transducer at room temperature and barometric pressure.
Deflection:
The change in length along the primary axis or distance a diaphragm moves at the center between no-load and rated load conditions.
Figure 3. Deflection Drawing

Diaphragm:
The sensing membrane that is deformed when pressure is applied.
Figure 4. Diaphragm Image

Excitation, Electrical:
The voltage or current applied to the input terminals of the transducer.
Flush Diaphragm:
Sensing element is located on the very tip of the transducer (NO pressure port).
Figure 5. Flush Diaphragm Image

Frequency Response:
The range of frequencies over which the transducer voltage output will follow the sinusoidally varying mechanical input within specified limits.
Full Scale:
See Rated Capacity.
Full Scale Output:
The algebraic difference between the minimum output (normally zero) and the rated capacity.
Gauge Pressure:
The pressure above (or below) atmospheric. It represents positive difference between measured pressure and existing atmospheric pressure. It can be converted to absolute by adding actual atmospheric pressure value.
Figure 6. Gauge Pressure Drawing

Gauge Pressure Transducer:
A transducer that measures pressure relative to the atmospheric pressure.
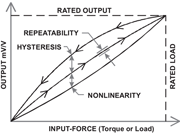
Hysteresis:
The maximum difference between output readings for the same measured point, one point obtained while increasing from zero and the other while decreasing from full scale. The points are taken on the same continuous cycle. The deviation is expressed as a percent of full scale.
Figure 7. Hysteresis Drawing
Input Impedance:
The resistance measured across the excitation terminals of a transducer at room temperature, with no load applied, and with the output terminals open circuited.
Insulation (Isolation) Resistance:
The DC resistance expressed in ohms measured between any electrical connector pin or lead wire and the transducer body or case. Normally measured at 50 VDC.
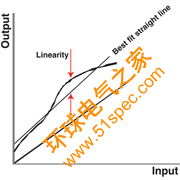
Linearity:
The maximum deviation of the calibration curve from a straight line between zero and full scale, expressed as a percent of full scale output and measured on increasing measured only.
Figure 8. Linearity Drawing
Line Pressure:
The maximum pressure in the pressure vessel or pipe for differential pressure measurement.
Load:
The weight, torque or force applied to the transducer.
Load Buttons:
A load button has a spherical-like shape on the top surface of a load cell where the load force is applied.
Figure 9. Load Button Image

Measured Media:
The physical quantity, property or condition that is measured (e.g., pressure, load, weight, acceleration).
Mounted Resonant Frequency:
The frequency at which the internal spring/mass system of an accelerometer resonates, producing a 90º phase shift in output signal versus applied acceleration.
Output:
The electrical signal measured at the output terminals that is produced by an applied input to a transducer.
Output Impedance:
The resistance as measured on the output terminals of a transducer at standard temperature, with no measured applied and with the excitation terminals open-circuited.
Overrange, Safe:
The maximum pressure or load that may be applied to the transducer without causing a permanent change in the performance specifications.
Phase Shift:
The phase angle between the output signal and the applied acceleration.
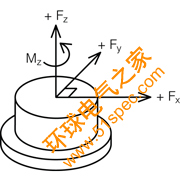
Primary Axis:
The axis along which the transducer is designed to be loaded; normally its geometric centerline.
Figure 10. Primary Axis Drawing
PSI:
Pounds per square inch.
PSIA:
Pounds per square inch absolute.
PSID:
Pounds per square inch differential.
PSIG:
Pounds per square inch gauge.
Pull Plate:
Load cell attachment allows tension or compression force to be directed at the center line of a load cell through a threaded-center hole.
Figure 11. Pull Plate Assembly Image

Range:
The measured values, over which a transducer is intended to measure, specified by their upper and lower limits.
Rated Capacity:
The maximum measurand that a transducer is designed to measure within its specification.
Repeatability:
The ability of a transducer to reproduce output readings when the same measured value is applied to it consecutively, under the same conditions, and in the same direction. Repeatability is expressed as the maximum difference between output readings as a percent of full scale.
Figure 12. Repeatability Drawing

Resolution:
The smallest change in mechanical input that produces a detectable change in the output signal.
Sensing Element:
The part of the transducer that reacts directly in response to the measurand.
Sensitivity:
The ratio of change in transducer output to a change in the value of the measurand.
Shunt CAL (R-CAL):
The change in electrical output caused by placing a fixed resistor between the appropriate transducer terminals. Used "in the field" for quick calibration.
Span:
The algebraic difference between the limits of the range from zero to full scale.
Specifications:
The group of error limits within which each device will operate.
Strain Gauge:
A measuring element for converting force, pressure, tension, etc., into an electrical signal.
Figure 13. Stain Gauge Drawing

Temperature, Compensated:
The range of temperature over which a transducer can operate up to full scale and still meet all specifications.
Temperature Compensation:
The utilization of supplementary devices, materials or components within the bridge to minimize sources of error caused by changing temperature.
Temperature, Operating:
The range of temperature over which a transducer may be safely operated up to full scale without causing failure, but specifications may not be met.
Temperature Effect On Span:
The change in rated output due to a change in ambient temperature. This is usually expressed as ± a percentage change in rated output per degree F change in ambient temperature, over the compensated temperature range.
Temperature Effects On Zero:
The change in zero balance due to a change in ambient temperature. This is usually expressed as ± a percentage change in rated output per degree F change in ambient temperature over the compensated temperature range.
Transducer:
A device (or medium) that converts energy from one form to another. The term is generally applied to devices that take physical phenomenon (pressure, temperature, humidity, flow, etc.) and convert it to an electrical signal.
Transmitter:
A transducer that has a 4-20 mA two-wire output.
Transverse Sensitivity:
Signal output as a result of acceleration perpendicular to the sensitive axis. Specified as a percentage of sensitive axis output for equivalent right angle acceleration or as a decimal fraction.
Vibration Error:
The maximum change in output of a transducer when a specific amplitude and range of frequencies are applied to a specific axis at room temperature.
Wet/Dry Differential:
A differential pressure transducer or transmitter that uses a metal diaphragm at the wet port where fluids can be applied, and no diaphragm at the dry port. The dry port exposes the internal circuitry to the medium, so only clean dry gas can be applied to this port.
Figure 14. Wet/Dry Differential Image

Wet/Wet Differential:
A differential pressure transducer or transmitter that has a metal diaphragm in each pressure port to permit fluid into both ports.
Figure 15. Wet/Wet Differential Image

Wetted Parts:
The diaphragm and pressure port material that comes in direct contact with the medium (gas, liquid).
Zero Adjustments:
Used when "setting up" a transducer to adjust the output signal to zero when zero load/pressure is applied.
Zero Balance:
The output signal of the transducer with rated excitation and with no load applied, usually expressed as a percent of rated output.
Zero Rerturn:
The difference in zero balance measured immediately before rated load application of specified duration and measured after removal of the load, and when the output has stabilized.


















